Table of Contents
- Introduction to Electrical Safety
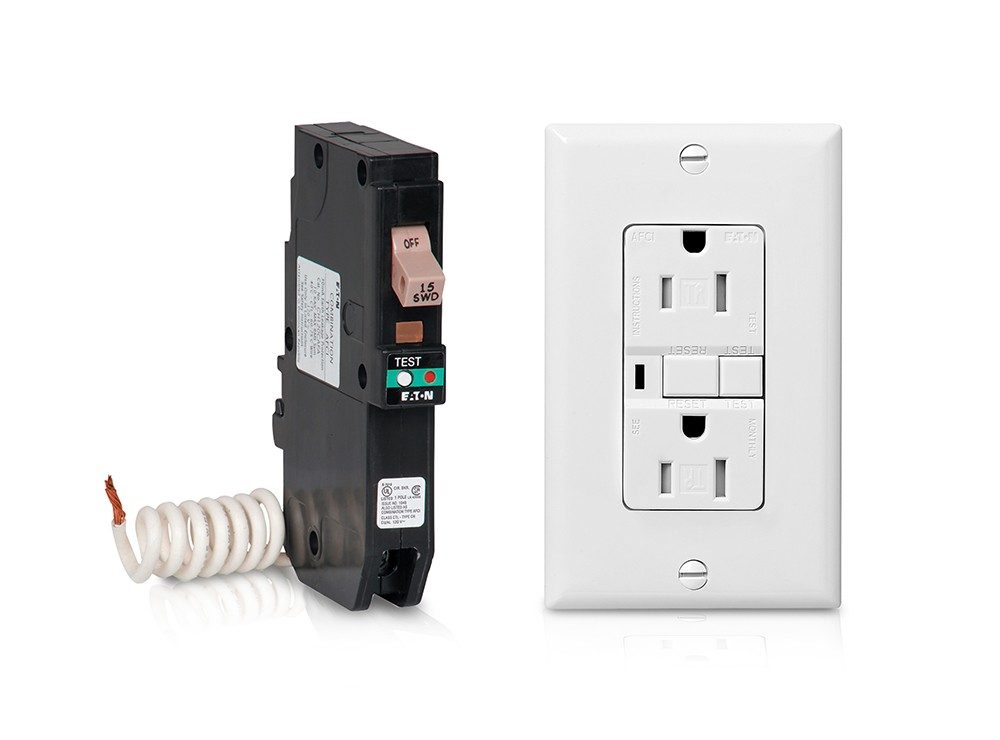
- Understanding GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters
- Decoding AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters
- Key Differences Between GFCI and AFCI
- How GFCI and AFCI Devices Work
- Installation Guidelines and Standards
- Common Questions about GFCI and AFCI
- Conclusion: Ensuring a Safer Environment
Introduction to Electrical Safety
In a world increasingly reliant on technology, electricity is a fundamental part of everyday life, powering everything from kitchen appliances to complex industrial machines. Yet, amidst its conveniences, electricity poses hazards that demand our attention and understanding. Prioritizing electrical safety is crucial for protecting individuals and infrastructure from threats like electric shocks and fires. Integrating safety devices such as GFCI and AFCI is paramount in reducing these dangers. An essential step in enhancing safety is grasping the difference between GFCI and AFCI, empowering us to create safer home and workplace environments.
These devices might seem complex, but they are vital for maintaining safety standards. They act as silent protectors, continuously monitoring electrical systems to prevent hazardous incidents before they occur. While often hidden behind walls or under circuit boards, GFCIs, and AFCIs are critical in safeguarding lives. Whether you’re upgrading a home, planning new construction, or simply passionate about safety, understanding these devices is beneficial. Knowing when and where to install them enhances safety and fosters a more secure living or working space.
Understanding GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters
GFCIs, or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters, are pivotal in protecting against the dangers of electric shock. These devices are specifically designed to monitor the balance of electrical current flowing in and out of a circuit. When they detect a slight imbalance, indicating a current leak, they promptly cut off power to prevent potential harm. This rapid response is vital in areas susceptible to water exposure, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor locations. In fact, according to OSHA, GFCIs are essential safety measures in construction environments where electrical incidents can have severe consequences. Due to their high risk, many building codes mandate GFCI tests. The significance of GFCIs is amplified in these moisture-prone environments, where they act as essential guardians against electrical shocks.
Decoding AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters
While GFCIs focus on preventing electric shocks, Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters, or AFCIs, are pivotal in mitigating the risk of electrical fires. Arc faults occur when electrical wiring is damaged, resulting in intermittent electrical discharges or arcs that can ignite nearby combustible materials. AFCIs are sensitive to these arcs, detecting their specific electrical patterns and shutting down the circuit before a fire can start. This prevention is especially critical in older buildings with aging wiring and homes with extensive electrical networks. Annually, electrical fires account for numerous residential fire incidents, making the role of AFCIs even more crucial in maintaining safety within both new and old infrastructures.
Key Differences Between GFCI and AFCI
Although GFCIs and AFCIs target distinct hazards, they are indispensable components of a comprehensive safety system. GFCIs are specially designed to prevent shocks in environments where water contact is likely, effectively reducing the risk of fatal accidents. In contrast, AFCIs are advocates for fire safety, focusing on detecting arc faults that could lead to devastating fires. According to Family Handyman, while these devices protect against different risks, installing GFCIs and AFCIs in the right locations is crucial for enhancing safety and complying with regulations. By addressing various aspects of electrical safety, GFCIs, and AFCIs complement each other perfectly. Installing both devices across a building meets regulatory standards and fortifies defense against electric shocks and potential fires. This dual protection approach is highly recommended for a safe and resilient electrical system.
How GFCI and AFCI Devices Work
The technologies behind GFCIs and AFCIs involve intricate systems prioritizing safety. GFCIs continuously monitor the electrical current’s balance, tripping the circuit upon detecting any discrepancies. This quick cutoff prevents leakage currents from causing injuries. On the other hand, AFCIs are equipped with sensors capable of distinguishing the electrical patterns typical of arc faults. When they detect such patterns, these devices quickly disconnect the circuit, averting potential fire hazards. Both devices share a common goal: preserving the safety and well-being of people and property by preemptively addressing existing and possible electrical anomalies.
Installation Guidelines and Standards
Proper installation of GFCI and AFCI devices is critical in ensuring their effectiveness and adherence to safety standards. Following the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines are essential for identifying the correct locations and methods for installing these devices. Whether updating the wiring in an older home or working on a new project, compliance with these guidelines ensures maximum protection. Professional installation by certified electricians guarantees that GFCIs and AFCIs function correctly, ultimately enhancing the facility’s electrical safety. Ensuring the devices are installed according to these codes is not just about compliance but also assigning them their full potential as safety devices.
Common Questions about GFCI and AFCI
- How often should GFCI and AFCI devices be tested? Although highly reliable, GFCIs and AFCIs require regular testing to maintain their protective function. It is advisable to test GFCI outlets at least monthly to confirm their operation. Manufacturers usually incorporate a test button on these devices, making it easy to perform regular checks. Pressing the button should trip the circuit, indicating its readiness to protect. AFCIs, much like GFCIs, should also be verified periodically. Regular inspections help identify any potential failures before they compromise protection. Routine checks and appropriate maintenance are crucial for keeping these devices in optimal working condition and ensuring maximum safety.
- Can GFCI and AFCI be used on the same circuit? Utilizing GFCI and AFCI devices on the same circuit is possible and advisable for comprehensive electrical safety. This combination provides a dual-layer defense, protecting against electric shock and fire hazards. While GFCIs mitigate shock risks, AFCIs address the fire risks associated with arc faults, creating a robust safety system. This approach is invaluable in maintaining a safe and supportive electrical infrastructure in shared environments, such as residential complexes or office buildings. Combining these devices effectively minimizes risks, furthers security, and protects occupants and property.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Safer Environment
Safeguarding the electrical environment in our homes and workplaces involves a multifaceted approach, with GFCI and AFCI devices playing pivotal roles. By incorporating these advanced technologies, everyday spaces are transformed into safer, more secure environments, free from the looming threats of electrical hazards. Adhering to installation guidelines and regularly testing these devices guarantees functionality, effectively contributing to the overall electrical safety strategy. Prioritizing us and AFCIs elevates internal safety standards and offers peace of mind, knowing that every precaution has been taken to protect people and property from unforeseen electrical events.